Light Bulb
Thomas & His Invention
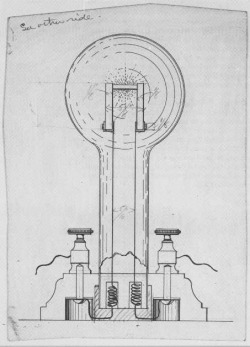
Edison's Incandescent light bulb is a source of electric light which works by driven heat light emissions. The base of the light bulb has two metal contacts, which connect to an electrical circuit. These contacts are attached to two wires, which are also attached to the filament; the filament is in the middle of the bulb, it is usually supported by a glass mount. Then a power supply sends electric currents from one contact to the other contact, they travel up through the wires and also the filament. As the current passes through the filament, it arouses the atoms that make up the filament material; this causes them to give off energy in the forms of heat and light.
Edison tried many different things for the filament but most produced light for only a short time. He then tried a carbonized cotton thread, this burned for hours. Soon, light bulbs were made using the metal tungsten for the filament, tungsten works well for light bulbs because of its high melting point.
By the year of 1882 in September Thomas Alva Edison had opened up his central station which he then supplied electricity for a whole square mile of New York. Edison used the method of Direct Current, some may know as DC. DC was used for generating and transmitting his electricity. Thomas Edison’s long lasting incandescent light bulb made history to all around and will to continue.
Edison tried many different things for the filament but most produced light for only a short time. He then tried a carbonized cotton thread, this burned for hours. Soon, light bulbs were made using the metal tungsten for the filament, tungsten works well for light bulbs because of its high melting point.
By the year of 1882 in September Thomas Alva Edison had opened up his central station which he then supplied electricity for a whole square mile of New York. Edison used the method of Direct Current, some may know as DC. DC was used for generating and transmitting his electricity. Thomas Edison’s long lasting incandescent light bulb made history to all around and will to continue.
